Domain Knowledge Prompt-driven Large Model with Few Labeling Data via Multi-task Learning for Assessment of Staple Crop Disease Severity (DKP-ADS)
Introduction
The DKP-ADS method is a comprehensive framework for assessing the severity of major crop diseases and extracting all-round crop information in a multi-task manner. The method consists of four main components: image information processor, lesion detector training, lesion and leaf segmenter, and disease severity assessor. The image information processor adopts a multi-task classification strategy to first classify the staple crops (e.g., corn, sorghum, potato, etc.), and then classify the specific diseases of each crop to obtain more detailed crop image information. The disease severity in the main crop images is then classified (e.g., severe, general, and healthy). This step addresses the challenge of SAM's inability to segment images with excessively high disease severity. Based on the initial classification, we train a prompt information model to generate accurate lesion clues to guide GroundingDINO to locate the lesion area. The lesion detector training uses the annotated lesion prompt information and plant disease images to fine-tune GroundingDINO, introduces agricultural professional domain knowledge, and makes GroundingDINO sensitive to special lesion content. The lesion and leaf segmenter adopts a dual-path strategy. On the one hand, the original GroundingDINO model is used to detect the leaf area, and on the other hand, the lesion area is detected based on the fine-tuned GroundingDINO to obtain accurate target boxes. These bounding boxes serve as cues to guide SAM to achieve accurate segmentation of leaves and lesion areas. Finally, the disease severity assessor calculates the proportion of the lesion area based on the leaf and lesion masks obtained by SAM, resulting in an accurate disease severity assessment.
Dependencies
- CUDA 11.8
- Python 3.8 (or later)
- torch==2.0.1
- torchaudio==2.0.2
- torchvision==0.15.2
- tsupervision==0.17.1
- numpy==1.23.5
- Pillow==10.3.0
- tqdm==4.65.0
- wheel==0.43.0
- scikit-image==0.21.0
- opencv-python==4.10.0.84
GitHub: https://github.com/GZU-SAMLab/DKP-ADS
Data
Our study focuses on identifying staple crop diseases and calculating the proportion of affected areas based on segmentation results to assess disease severity. To ensure the reliability and effectiveness of the method, we construct a series of carefully designed datasets that cover a wide range of crop types and disease categories, optimized for various application scenarios. The multi-task acquisition of crop image information is realized, which lays a foundation for subsequent lesion detection, segmentation, and grading. We propose a staple crop image database by drawing from open-source agricultural data websites and relevant literature, including resources such as the Plant village dataset, PDDD dataset, Wheat Leaf dataset, Corn Leaf Infection dataset, and Riccleafs dataset etc. The database includes seven staple crops, such as rice, sorghum, corn, sweet potato, wheat, soybean, and potato, covering 79 disease categories, with a total of 37,594 images for disease identification
The code can be downloaded from there. The datasets can be download from there. The training set will be made public when the paper is accepted.
Pre-trained weights
Some pre-trained model weights are uploaded. You can download it.
Get Started
Fine-tuning GroundingDINO
cd /Grounding-Dino-FineTuning
python train.py
Predict
cd /main
python predict.py
Validation
cd /main
python val.py
Batch image segmentation and grading
cd /main
python main.py
Results
Experimental results comparing the segmentation performance of different models.
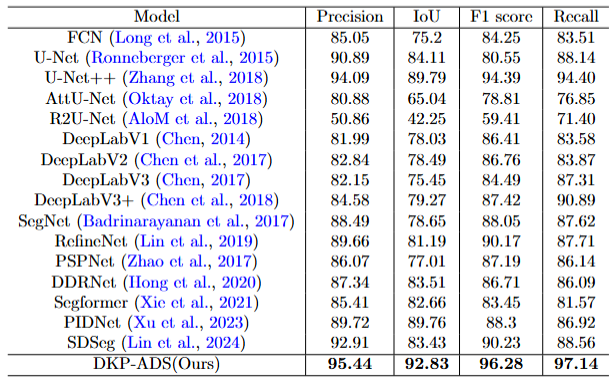
Table 1: Experimental results comparing the segmentation performance of different models. The evaluation metrics include Precision, IoU, F1 score, and Recall.
Visualization of Lesion Segmentation
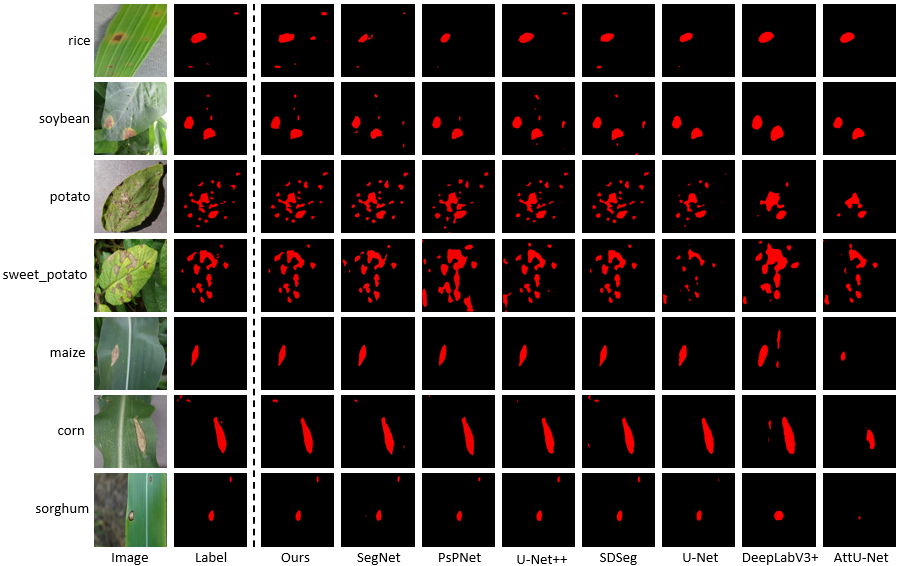
Figure 1: Comparison of the results of lesion segmentation. We compare the disease segmentation results of our method with those of other methods for seven major staple crops. Our results show that our method closely aligns with the ground truth labels and exhibits significant advantages over other models.
Experimental results comparing the classification performance of different models.
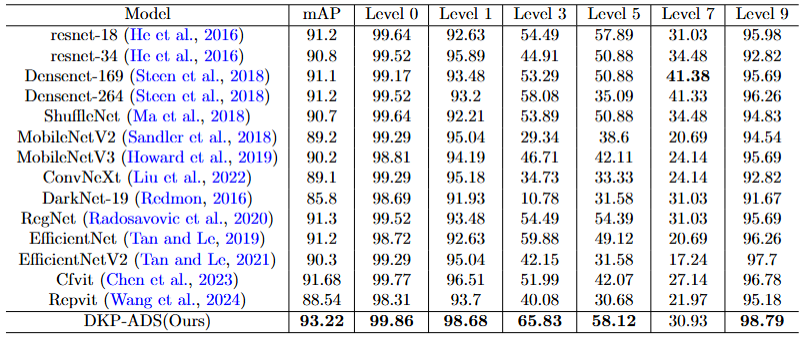
Figure 2: Experimental results comparing the classification performance of different models. The dataset used in this experiment contains seven staple crops, and we compare the classification accuracy of our method with other classification methods. The mAP shows the average accuracy of all levels.
Evaluation of Specific Staple Crops(Potato and Cron).
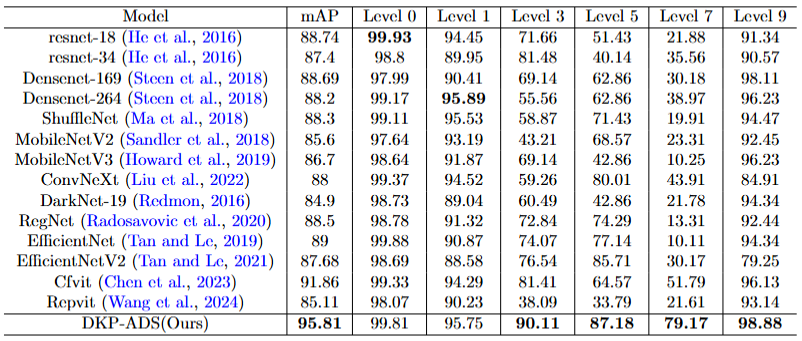
Figure 3: Experimental results of grading evaluation of single crop potato with other classification models. We separately compare the performance of our method on potato with other classification models, where mAP represents the average accuracy across all levels.
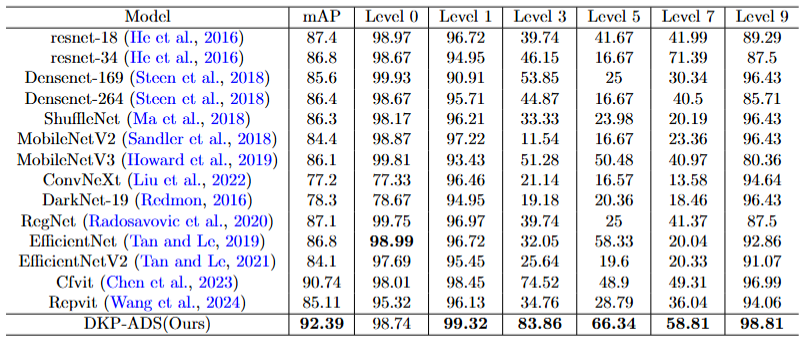
Figure 4: Experimental results of grading evaluation of single crop corn with other classification models. We separately compare the performance of our method on corn with other classification models, where mAP represents the average accuracy across all levels.
