DKP-ADS: Domain Knowledge Prompt-driven Large Model with Few Labeling Data via Multi-task Learning for Assessment of Staple Crop Disease Severity. In modern agricultural practices, the invasion of plant diseases can lead to severe food crises, making disease management crucial. Effective disease management requires accurate identification of disease types and assessment of their severity. At present, the mainstream methods for disease severity grading involve obtaining disease segmentation regions and calculating their area proportion on the leaves, or directly using classification networks to assess disease severity. However, these methods require large amounts of labeled data for training, and direct use of classification networks for disease severity classification does not quantify the proportion of lesions, leading to inaccurate results. To address these issues, we propose an automated framework for major crop disease grading that combines multi-task learning and knowledge-driven large model segmentation techniques. This framework includes four modules: image information processor, lesion detector training, lesion and leaf segmenter, and disease severity assessor. Additionally, we bulid a database of leaf images of major crop diseases and annotated part of the data. Extensive experiments on this database show that our framework can accurately identify and assess the types and severity of diseases in major crops, even without the need for extensive data labeling.
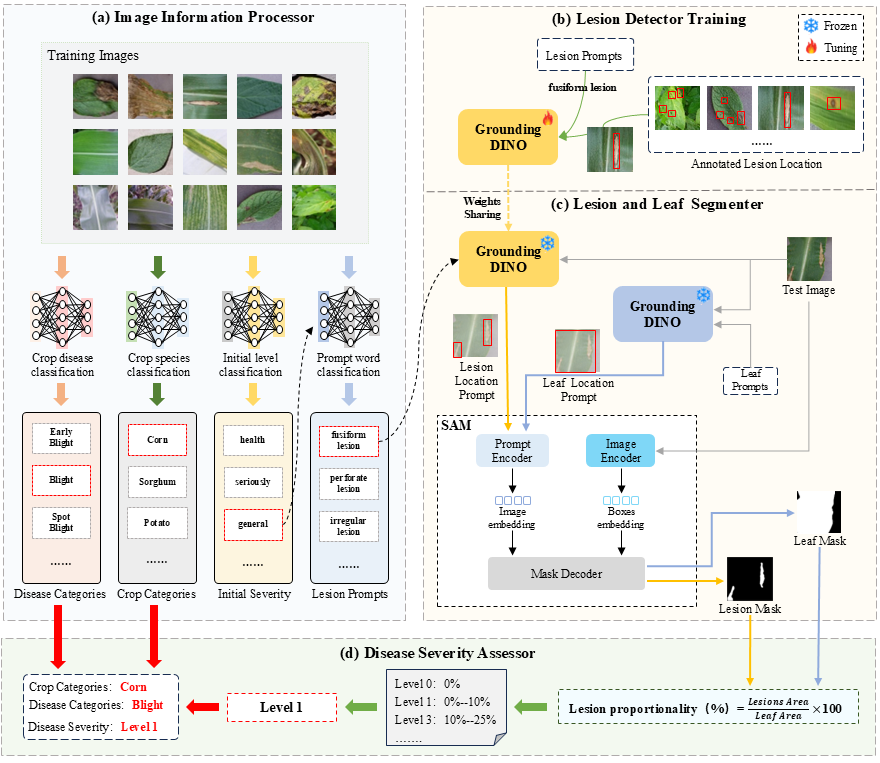
Figure 1: Framework of the proposed method. (a) Image Information Processor, utilizing the multi-task learning to extract image information. (b) Lesion Detector Training, introducing specialized domain knowledge for fine-tuning models. (c) Lesion and Leaf Segmenter, using the trained model to segment the lesions and leaves. (d) Disease Severity Assessor, determine a disease diagnosis by calculating the proportion of the lesion area.
A schematic diagram of introducing disease domain knowledge based on GroundingDINO A schematic diagram of introducing disease domain knowledge based on GroundingDINO is illustrated in Figure 2. The model receives inputs of images and lesion information, extracting features from both through an image encoder and a text encoder, respectively. Subsequently, these features undergo enhancement via a feature enhancer to improve the quality of the feature representations. Following this, the refined textual features guide the refinement of visual query vectors, generating image region query vectors that are strongly associated with the textual features. Finally, the enhanced image features, enhanced textual features, and refined visual query vectors are fed into a decoder together, which outputs the detection results of target regions.
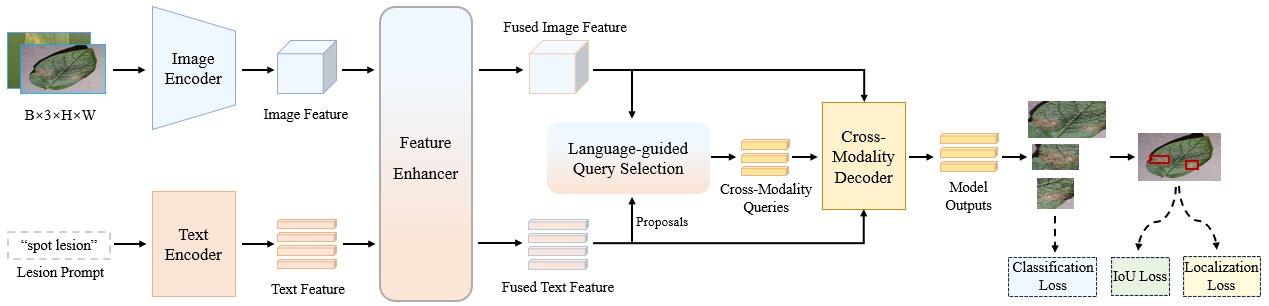
Figure 2: A schematic diagram of introducing disease domain knowledge based on GroundingDINO. and the feature enhancer enhances the two features, extracts the relevant semantic information of the image under the guidance of the text features, and finally identifies the focal area.
DKP-ADS method Evaluation Process To achieve high performance in staple crop disease severity assessment, the Evaluation process of the DKP-ADS method is end-to-end, consisting of six steps, as shown in Figure 3.
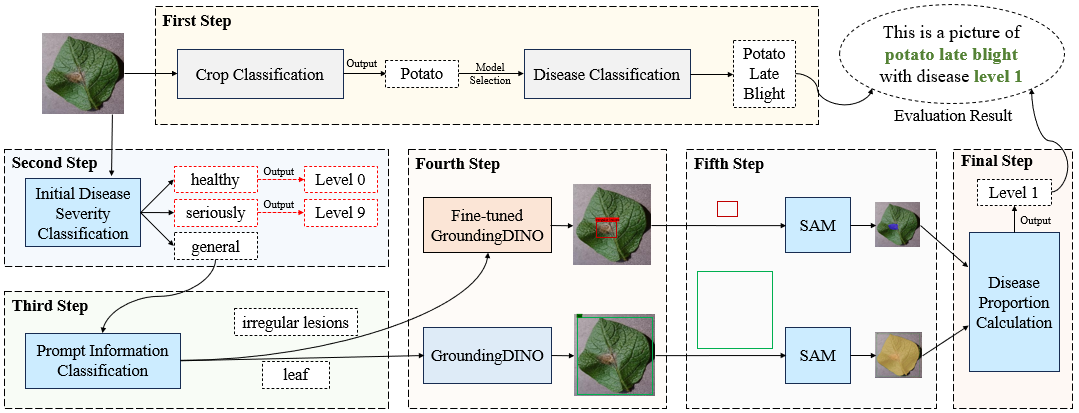
Figure 3: Evaluation Process. The DKP-ADS method is divided into 6 steps during testing. The first step achieves crop and disease classification, the second step achieves initial severity classification, the third step generates lesion prompt information, the fourth step detects lesions and leaf positions, the fifth step segments leaf and lesion regions, and the final step performs grading.
